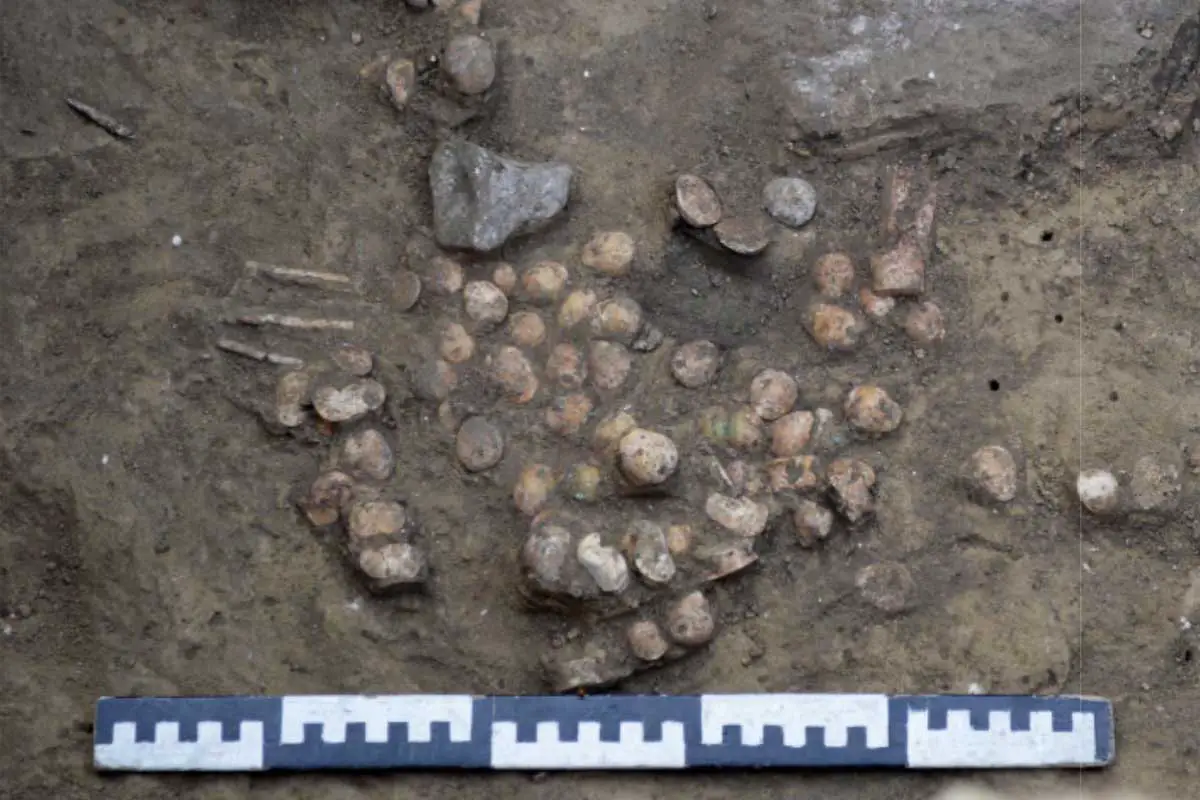
Amber, a fossilized tree resin, has been highly valued by ancient civilizations for its beauty, rarity, and mystical properties. Used in jewelry, trade, and religious rituals, amber played a significant role in the cultural and economic life of many ancient societies.
Amber in Jewelry and Adornment
Amber was widely used in jewelry, often carved into intricate beads, pendants, and amulets. The warm, golden hues of amber made it a prized material among the elite, symbolizing wealth and status. The Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans crafted elaborate amber ornaments, believing in its protective and healing properties.
Amber as a Valuable Trade Commodity
Amber was a crucial trade good in the ancient world, with extensive trade routes known as the Amber Road connecting the Baltic region, where much of the world’s amber was sourced, to the Mediterranean and beyond. The Romans highly valued Baltic amber, importing large quantities to use in luxury goods and medicine. Amber’s rarity and desirability made it a medium of exchange and a symbol of prosperity.
Ritual and Spiritual Significance
Beyond its decorative and economic value, amber held deep spiritual significance. Many cultures believed it had protective and healing powers. In ancient Greece and Rome, amber was associated with the sun god and thought to contain divine energy. The Egyptians placed amber in tombs to guard the deceased in the afterlife, while some early European tribes burned amber as incense in sacred ceremonies.
Amber’s Lasting Legacy
The reverence for amber continued into the Middle Ages and beyond, influencing modern jewelry and alternative medicine. Today, amber remains a sought-after material, prized for its historical significance and natural beauty.
Conclusion
Amber’s role in ancient societies extended far beyond ornamentation. It was a symbol of wealth, a valuable trade item, and a powerful spiritual substance. The enduring fascination with amber underscores its importance as a link between nature, culture, and human history.